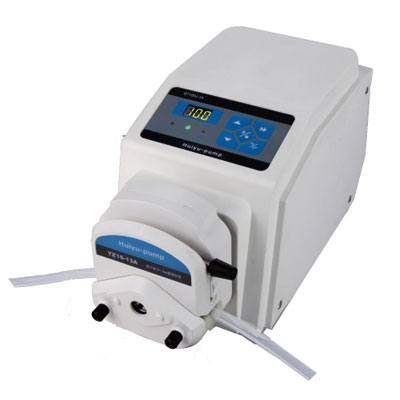
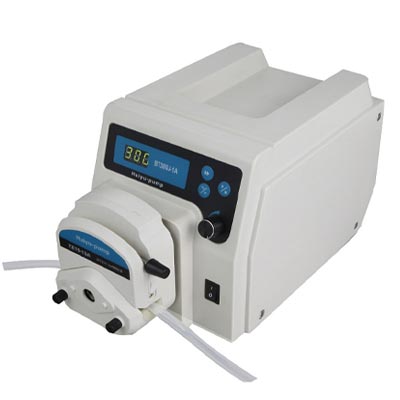
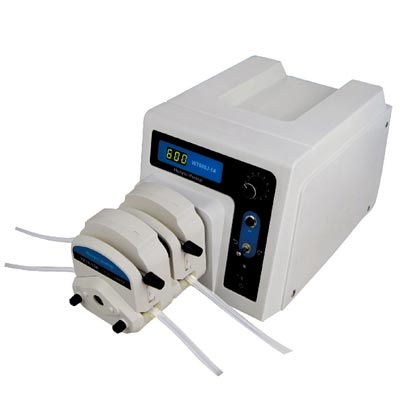
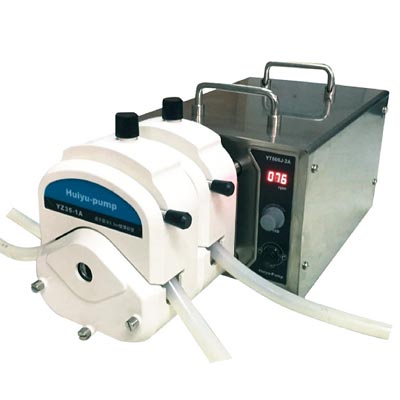
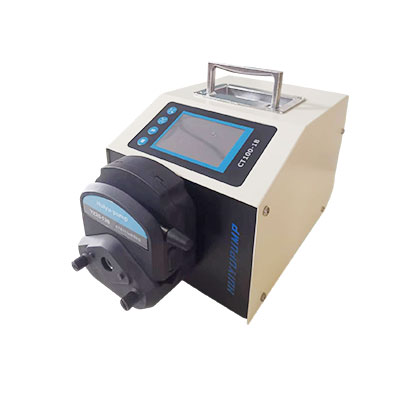
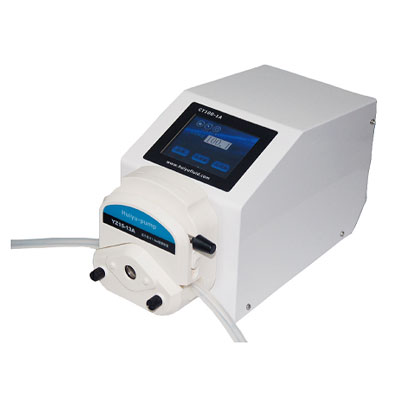
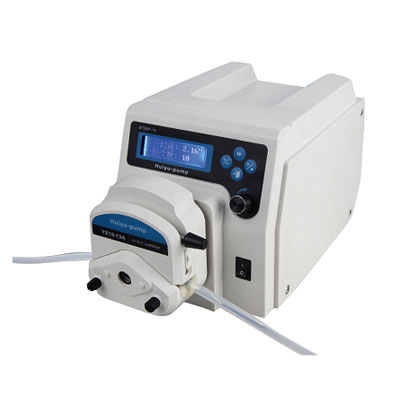
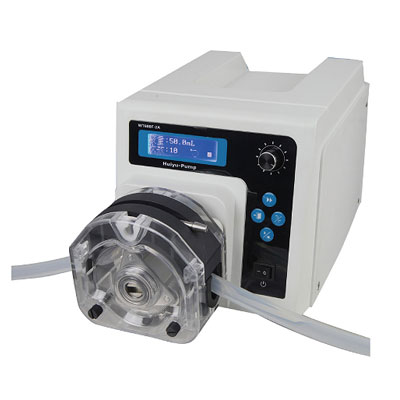
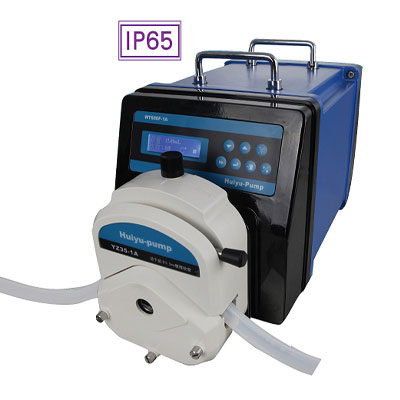
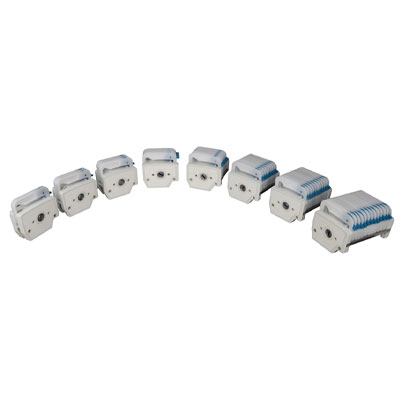
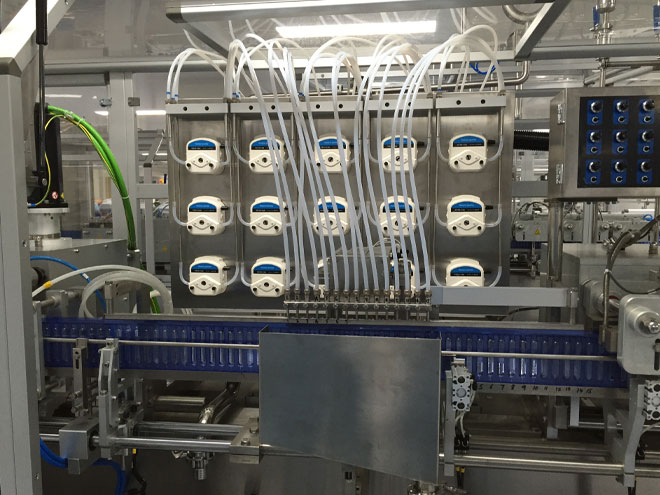
(1) Hose characteristics:
• The pump tube has a certain degree of elasticity, that is, the hose can quickly recover its shape after being compressed radially (Shore hardness: 40 ~ 80).
• Have a certain ability to withstand pressure
• No leakage (good air tightness), low adsorption
• Good temperature resistance, not easy to age
• No swelling, anti-corrosion
• Low precipitation
(2) Chemical compatibility:
When transferring different fluids, the hose should exhibit certain excellent chemical properties, which is called chemical compatibility. Such as: low adsorption, good temperature resistance, resistance to aging, no swelling, corrosion resistance, low precipitation, etc.
(3) Chemical resistance:
The chemical resistance of the hose decreases with the increase of temperature. Chemicals that have no effect on the pipe at room temperature may affect the hose with the increase of temperature. When transferring different fluids, the hose should exhibit certain excellent chemical properties.
Chemical compatibility test: Take a section of sample tube, record its weight, diameter, length and other parameters, immerse the sample tube in a closed container filled with liquid, soak for at least 48 hours, take out the sample tube, wash it with water, and dry it. Re-measure its weight, diameter and length and observe the changes; at the same time, check whether the hose becomes soft or brittle. If there is any change, it means that the hose is chemically affected by the liquid, that is, the hose is not compatible with the liquid. Each candidate pump tube sample should be put into the factory's actual environmental conditions for trial operation, and the test results should be closely observed. If the pump tube does not show discoloration, swelling, cracks, loss of fluidity, or other signs of deterioration after trial operation, it is proved that it is compatible with the fluid.
(4) Under pressure:
When a pump pushes fluid through a filter, or pushes fluid through a flow meter or valve, or pumps fluid into a pressurized reaction vessel, back pressure is created. The application of peristaltic pumps is limited by the pressure-bearing performance of the hose. If the system pressure exceeds the limit pressure of the hose, the hose will expand, causing excessive wear of the hose or rupture of the hose. The factors that affect the pressure of the hose are: material, the ratio of diameter to wall thickness, and so on.
(5) Temperature:
The adaptability of the hose to the operating temperature range is a factor to be considered by the user. Different materials have different temperature performance. Some pipes, such as silicone rubber, have a wide temperature tolerance range and are suitable for both high and low temperature processes; while some pipes are only suitable for a small temperature range. Before selecting the pipe, the user should first find out the maximum temperature and the minimum temperature in the system, and then ensure that the selected pump pipe works in this temperature range.
(6) Size:
The size of the hose directly affects the flow rate, the inner diameter of the hose determines the flow rate, and the inner diameter is directly proportional to the flow rate. Wall thickness affects the ability of the hose to be compressed and rebound, and also has a great impact on the life of the hose. Please refer to the "Hose Specifications" table.
(7) Transparency:
Whether a transparent pipe should be used depends on whether the operator needs to observe the condition of the fluid in the pipe at any time, and also whether the fluid is sensitive to light. If the operator needs to observe the fluid, bubbles, particles, pollution, etc. in the tube at any time, he should choose a transparent tube such as Tygon polyethylene or silicone rubber; and if the solution is not suitable for exposure, he should choose an opaque tube.
(8) Air permeability:
For some gas-sensitive fluids, such as fluids that are susceptible to oxidation, or anaerobic cell culture fluids, users should consider the air permeability of the pipeline. In general, the air permeability of the silicone tube is high. Therefore, for fluids that are not suitable for contact with gas, pipes with lower air permeability should be used.
(9) Certification:
When hoses are used for related purposes, relevant certifications may be required. Such as the United States Pharmacopoeia standard USP, the European Pharmacopoeia standard EP, the United States Food and Drug Administration standard FDA, the United States Department of Agriculture standard USDA and the National Sanitation Foundation standard NSF.
(10) The life of the hose:
Different hoses have different ability to withstand repeated squeezing and friction of rollers. Different tube types, pipe materials, pump heads, and operating speeds have different life spans. Choose long-life, thick-walled pipes and large-flow pumps, and run at lower speeds to obtain longer hose life.
(11) Flow range:
Each hose corresponds to a fixed speed range, and we select the corresponding hose according to the flow range required by the customer. For specific data, see "Peristaltic Pump Hose"
 Your location:
Your location:
 400-0602-365
400-0602-365